On May 3, 2023, Surgeon General Vivek Murthy issued an advisory raising an alarm about what he called an “epidemic of loneliness” in the United States.
Now, I am not saying that Vivek Murthy read my book, How Medicine Works and When It Doesn’t — released in January and available in bookstores now — where, in chapter 11, I call attention to the problem of loneliness and its relationship to the exponential rise in deaths of despair. But Vivek, if you did, let me know. I could use the publicity.
No, of course the idea that loneliness is a public health issue is not new, but I’m glad to see it finally getting attention. At this point, studies have linked loneliness to heart disease, stroke, dementia, and premature death. And now, according to a new study, loneliness may be linked to Parkinson’s disease.
The UK Biobank is really a treasure trove of data for epidemiologists. I must see three to four studies a week coming out of this mega-dataset. This one, appearing in JAMA Neurology this week, caught my eye for its focus specifically on loneliness as a risk factor — something I’m hoping to see more of in the future.
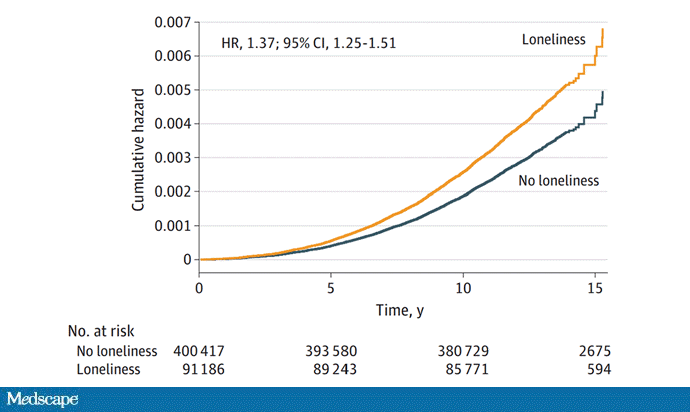
The study examines data from just under 500,000 individuals in the UK who answered a survey including the question “Do you often feel lonely?” between 2006 and 2010; 18.4% of people answered yes. Individuals’ electronic health record data were then monitored over time to see who would get a new diagnosis code consistent with Parkinson’s disease. Through 2021, 2822 people did — that’s just over half a percent.
So, now we do the statistics thing. Of the nonlonely folks, 2273 went on to develop Parkinson’s disease. Of those who said they often feel lonely, 549 people did. The raw numbers here, to be honest, aren’t that compelling. Lonely people had an absolute risk for Parkinson’s disease about 0.03% higher than that of nonlonely people. Put another way, you’d need to take over 3000 lonely souls and make them not lonely to prevent one case of Parkinson’s disease.
Still, the costs of loneliness are not measured exclusively in Parkinson’s disease, and I would argue that the real risks here come from other sources: alcohol abuse, drug abuse, and suicide. Nevertheless, the weak but significant association with Parkinson’s disease reminds us that loneliness is a neurologic phenomenon. There is something about social connection that affects our brain in a way that is not just spiritual; it is actually biological.
Of course, people who say they are often lonely are different in other ways from people who report not being lonely. Lonely people, in this dataset, were younger, more likely to be female, less likely to have a college degree, in worse physical health, and engaged in more high-risk health behaviors like smoking.
The authors adjusted for all of these factors and found that, on the relative scale, lonely people were still about 20%-30% more likely to develop Parkinson’s disease.
So, what do we do about this? There is no pill for loneliness, and God help us if there ever is. Recognizing the problem is a good start. But there are some policy things we can do to reduce loneliness. We can invest in public spaces that bring people together — parks, museums, libraries — and public transportation. We can deal with tech companies that are so optimized at capturing our attention that we cease to engage with other humans. And, individually, we can just reach out a bit more. We’ve spent the past few pandemic years with our attention focused sharply inward. It’s time to look out again.