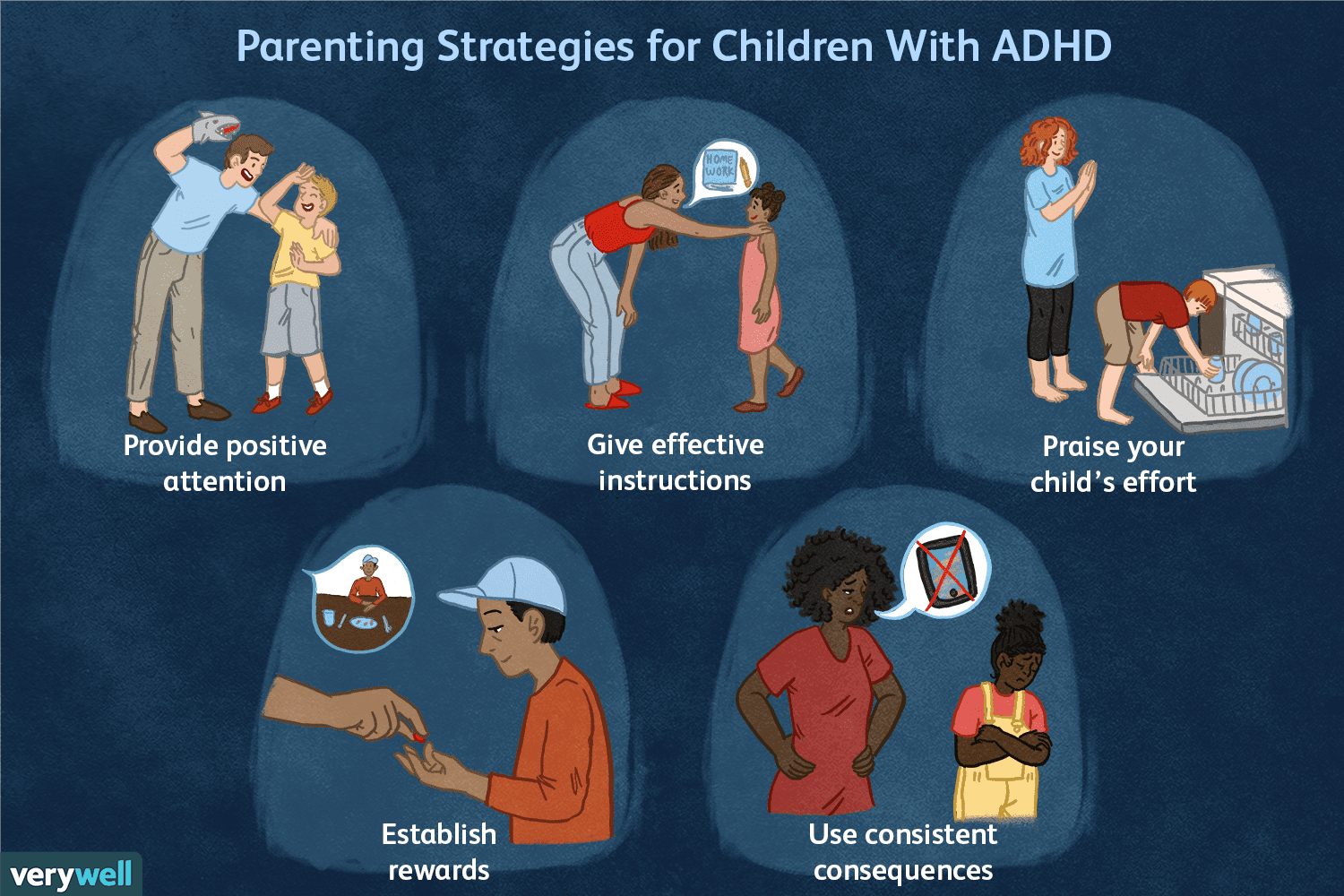
Have you ever met someone who seems easily distracted, constantly fidgeting, or struggles to finish what they start? Maybe that person is your child—or maybe it’s you. These could be signs of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) or Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD), and no, it’s not just a childhood condition.
Let’s break it down in simple terms: what ADHD really is, how it shows up in different age groups, and how it can be managed.
What is ADHD/ADD?
ADHD, short for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects focus, impulse control, and activity levels. ADD is an older term often used to describe a type of ADHD where hyperactivity isn’t as obvious. Today, all types fall under the ADHD umbrella, just with different presentations.
There are three main types:
- Inattentive type (what many still call ADD)
- Hyperactive-Impulsive type
- Combined type
ADHD in Children
In kids, ADHD can be easy to spot—or easy to miss. Some children may be hyperactive and impulsive, while others are just quietly inattentive.
🔍 Common signs in children include:
- Trouble paying attention in class
- Forgetting instructions or homework
- Constant fidgeting or squirming
- Interrupting others
- Struggling with organization or time management
It’s important to remember that all kids get distracted or hyper sometimes. What sets ADHD apart is that the symptoms are consistent, long-lasting, and interfere with everyday life.
ADHD in Adults
Surprisingly, many people aren’t diagnosed with ADHD until adulthood. Adult ADHD can look different than it does in kids, and it’s often misunderstood or mistaken for anxiety or laziness.
🧠 Common signs in adults:
- Difficulty focusing or finishing tasks
- Chronic procrastination
- Restlessness or difficulty relaxing
- Impulsive decisions (including financial or relationship-related)
- Feeling disorganized or overwhelmed easily
Many adults with ADHD had it as kids but were never diagnosed. As life gets more complex, the symptoms become harder to manage without support.
What Causes ADHD?
There’s no single cause of ADHD, but research points to a combination of genetic, neurological, and environmental factors. It tends to run in families, and differences in brain structure and function also play a role.
How is ADHD Diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually involves a comprehensive evaluation by a mental health professional or pediatrician. It may include questionnaires, interviews, and observation. There’s no single test for ADHD, which is why a detailed assessment is so important.
Managing ADHD: Treatment & Support
The good news? ADHD is manageable. With the right strategies and support, both kids and adults can thrive.
✅ Treatment options include:
- Behavioral therapy (especially helpful for children)
- Medication (like stimulants or non-stimulant alternatives)
- Coaching and counseling
- Routine and structure
- Healthy lifestyle choices like sleep, exercise, and nutrition
Support at school, at work, and at home can make a world of difference. The goal is not to “fix” someone—but to give them the tools they need to succeed.
Final Thoughts:
ADHD doesn’t define a person—it’s just part of their story. Whether you’re raising a child with ADHD or navigating it yourself as an adult, understanding is the first step. With patience, education, and the right support system, people with ADHD can live focused, fulfilling, and successful lives.
If this sounds like something you or your child is experiencing, don’t hesitate to talk to a healthcare provider. Early support can change everything.